The layout of a Diversion Head Works and its components
A typical layout of a canal head-works is shown in the figure below. Such a head-works consists of:
1.Weir proper
2.Under-sluices
3.Divide wall
4.River Training works
5.Fish Ladder
6.Canal Head Regulator
7.River Training Works e.g. Guide bank, Marginal bunds, spur and groyne, etc.
8.Shutters and Gates Silt
9.Regulation Works
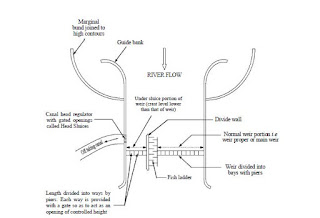 |
| Typical layout of diversion head-works |
Weir Proper:
It is a barrier constructed across the river. It aims to raise the water level in order to feed the canal.
Under-sluices:
The under sluices are the openings provided at the base of the weir or barrage. These openings are
provided with adjustable gates. Normally, the gates are kept closed. The crest of the under-under sluice
portion of the weir is kept at a lower level (1 1.5 m) than the crest of the normal portion of the weir. The
suspended silt goes on depositing in front of the canal head regulator. When the silt deposition becomes
appreciable the gates are opened and the deposited silt is loosened with an agitator mounting on a boat.
The muddy water flows towards the downstream through the scouring sluices. The gates are then closed. But, during the period of flood, the gates are kept open.
The main functions of under-sluices are:
1.To maintain a well defined deep channel approaching the canal head regulator.
2.To ensure easy diversion of water into the canal through the canal head regulator even during low
flow.
3.To control the entry of silt into the canal
4. To help to scour and of the silt deposited over the under-sluice floor and removing towards the downstream side.
5.To help passing the low floods without dropping the shutters of the weir.
The divide wall:
The divide wall is a masonry or concrete wall constructed at right angle to the axis of the weir.
The divide wall extends on the upstream side beyond the beginning of the canal head regulator; and on the
downstream side, it extends upto the end of the loose protection of the under-sluices.
The divide wall is a long wall constructed at right angles in the weir or barrage, it may be
constructed with stone masonry or cement concrete. On the upstream side, the wall is extended
just to cover the canal head regulator and on the downstream side, it is extended up to the
launching apron.






No comments:
Post a Comment
If you are getting more information from civilengineerfriend page please give your comments. Share the page information in your whatsapp group. Subscribe our page to get more information.