TYPES OF WINDOWS
Depending upon the manner of fixing, materials used for construction, nature of the operational
movements of shutters , etc., the common varieties of windows used in the building can be
grouped as follows:
1. Casement windows
2. Sliding windows
3. Metal windows
4. Corner windows
5. Gable windows bay windows
6. Lantern or lantern lights
7. Skylights
CASEMENT WINDOWS:
These are the windows, the shutters of which open like doors. The construction of a
casement window is similar to the door construction.
SLIDING WINDOWS:
These windows are similar to the sliding doors and the shutters moves on the roller bearings,
either horizontally or vertically. Such windows are provided in trains, buses, bank counter, shops
etc.
METAL WINDOWS:
These are now a days widely used, especially for public building. The metal used in construction
may be mild steel, bronze, or other alloys. The metal frame may be fixed direct to the wall or it
may be fixed on a wooden frame.
CORNER WINDOWS:
These windows are provided at the corner of a room .They are placed at the corner of the room
and thus they have two faces in two perpendicular direction. Due to such situation,there is entry
of light and air from two direction and in many cases , the elevation of building is also improved.
GABLE WINDOWS:
These are the windows which are provided in the gable ends of a roof.
BAY WINDOWS:
These windows project outside the external wall of a room. They maybe square , splayed,
circular, polygonal or of any shape. The projection of bay windows may start from floor level or
sill level. These windows admit more lights, increase opening area , provide ventilation and
improve the appearance of building.
LANTERNS:
These are the windows which are fixed on flat roofs to provide light to the inner portion of
building where light coming from external windows are insufficient. They maybe square or
rectangular or curved.
SKYLIGHTS:
these are the windows which are provided on the sloping surface of a pitched roof. The common
rafter are suitably trimmed and the skylight is erected on a curb frame. As skylight are mainly
meant for light, they are usually provided with the fixed glass panel.
TYPES OF DOORS
A door is a moving structure used to block off, and allow access to, an entrance to or within an
enclosed space, such as a building or vehicle. Similar exterior structures are called gate.
Typically doors have an interior side that faces the inside of a space and an exterior side that
faces the outside of that space. While in some cases the interior side of a door may match its
exterior side, in other cases there are sharp contrasts between the two sides, such as in the case of
the vehicle door. Doors normally consist of a panel that swings on hinges or that slides or spins
inside of a space.
Panel doors:
Panel doors, also called stile and rail doors, are built withframeand panel construction.
EN 12519 is describing the terms which are officially used in European Member States. The
main parts are listed below:
• Stiles - Vertical boards that run the full height of a door and compose its right and left
edges. The hinges are mounted to the fixed side (known as the "hanging stile"), and the
handle, lock, bolt, and/or latch are mounted on the swinging side (known as the "latch
stile".
Rails- Horizontal boards at the top, bottom, and optionally in the middle of a door that
join the two stiles and split the door into two or more rows of panels. The "top rail" and
"bottom rail" are named for their positions. The bottom rail is also known as "kick rail".
A middle rail at the height of the bolt is known as the "lock rail", other middle rails are
commonly known as "cross rails".
• Mullions - Smaller optional vertical boards that run between two rails, and split the door
into two or more columns of panels, the term is used sometimes for verticals in doors, but
more often (UK and Australia) it refers to verticals in windows.
• Muntin - Optional vertical members that divide the door into smaller panels.
• Panels - Large, wider boards used to fill the space between the stiles, rails, and mullions.
The panels typically fit into grooves in the other pieces, and help to keep the door rigid.
Panels may be flat, or in raised panel designs. Can be glued in or stay as a floating panel.
• Light or Lite - a piece of glass used in place of a panel, essentially giving the door a
window.
Plank and batten doors:
Plank and batten doors are an older design consisting primarily of vertical slats:
• Planks - Vertical boards that extend the full height of the door, and are placed side by
side filling the door's width.
• Battens - Smaller slats that extend horizontally across the door which the planks are
affixed to. The battens hold the planks together. Sometimes a long diagonal slat or two
are also implemented to prevent the door from skewing. On some doors, especially
antique ones, the battens are replaced with iron bars that are often built into the hinges as
extensions of the door-side plates.
Ledged and braced doors:
This type consists of vertical tongue and grooved boards held together with
battens and diagonal braces.
Frame and filled doors:
This type consists of a solid timber frame, filled on one face, face with Tongue and Grooved
boards. Quite often used externally with the boards on the weather face.
Flush doors:
A flush door consists of a framework of rails and styles and it is covered with plywood. There
are two varieties of flush doors
1.framed flush door :
It consists of styles, rails, horizontal ribs, vertical ribs, and plywood. As shown in fig.
2.laminated flush door
It consists of styles, rails, laminated core and plywood as shown in fig.
Louvered Doors:
In this type of doors, the shutters are provided with louvers, either fully or partly. The louvers are
arranged at such an inclination that horizontal vision is obstructed. The louvers maybe movable
or fixed as shown in fig.
Collapsible Steel Doors:
It consists of a mild steel frame. A collapsible steel door works without hinges and it is used for
compound gates, residential building , schools, sheds, godowns , workshop, public building , etc.
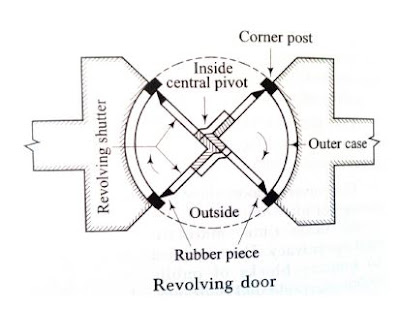
Revolving Doors:
It essentially consists of a centrally placed mullion in a circular opening revolving shutters which
are 4 in number are radially attached to pivot as shown in fig.
Read More
1. Plastering
Method of Plastering and Different plastering techniques
2. HOW
TO CALCULATE SHUTTERING AREA
4. Repair
and building repairs related to repair
5. Stones
Defination and site for Quarry with Hand Tools? Methods of quarrying
6. Timber
Details of structure and Different methods of seasoning
7. Foundation
and their types of Foundation
8. Types
of windows and Doors and their Specification





















No comments:
Post a Comment
If you are getting more information from civilengineerfriend page please give your comments. Share the page information in your whatsapp group. Subscribe our page to get more information.