Introduction:
The term "soil" can have different meanings, depending upon the field in which it is considered.
To a geologist, it is the material in the relative thin zone of the Earth's surface within which roots occur, and which are formed as the products of past surface processes. The rest of the crust is grouped under the term "rock"
To a pedologist,it is a substance existing on the surface ,with supports plant life
To an engineer ,it is material that can be:
built on: foundations of buildings, bridges
built in: basements, culverts, tunnels
built with: embankments, roads, dams
supported: retaining walls
Soil Mechanics is a discipline of Civil Engineering involving the study of soil, its behavior and its application as an engineering material.
Soil Mechanics is the application of laws of mechanics and hydraulics to engineering problems dealing with sediments and other unconsolidated accumulations of solid particles, which are produced by the mechanical and chemical disintegration of rocks, regardless of whether or not they contain an admixture of organic constituents.
Soil consists of a multiphase aggregation of solid particles, water, and air. This fundamental composition gives rise to unique engineering properties, and the description of its mechanical behavior requires some of the most classic principles of engineering mechanics.
Engineers are concerned with soil's mechanical properties: permeability, stiffness, and strength. These depend primarily on the nature of the soil grains, the current stress, the water content and unit weight.
Formation of Soils:
Soil is formed from rock due to erosion and weathering action. Igneous rock is the basic rock formed from the crystallization of molten magma. This rock is formed either inside the earth or on the surface. These rocks undergo metamorphism under high temperature and pressure to form Metamorphic rocks. Both Igneous and metamorphic rocks are converted in to sedimentary rocks due to transportation to different locations by the agencies such as wind, water etc. Finally, near the surface millions of years of erosion and weathering converts rocks in to soil
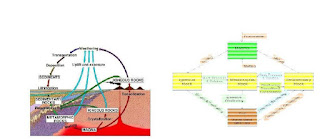 |
| Geologic Cycle of Soil |
Soils are formed from materials that have resulted from the disintegration of rocks by various processes of physical and chemical weathering. The nature and structure of a given soil depends on the processes and conditions that
formed it:
Breakdown of parent rock: weathering, decomposition, erosion.
Transportation to the site of final deposition: gravity, flowing water, ice, wind.
The environment of final deposition: flood plain, river terrace, glacial moraine, lacustrine or marine.
Subsequent conditions of loading and drainage: little or no surcharge, heavy surcharge due to ice or
overlying deposits, change from saline to freshwater, leaching, contamination.
All soils originate, directly or indirectly, from different rock types.
Weathering:
Physical weathering reduces the size of the parent rock material, without any change in the original composition of the parent rock. Physical or mechanical processes taking place on the earth's surface include the actions of water, frost, temperature changes, wind, and ice. They cause disintegration and the products are mainly coarse soils.
The main processes involved are exfoliation, unloading, erosion, freezing, and thawing. The principal cause is climatic change. In exfoliation, the outer shell separates from the main rock. Heavy rain and wind cause erosion of the rock surface. Adverse temperature changes produce fragments due to different thermal coefficients of rock minerals. The effect is more for freeze-thaw cycles.
Chemical weathering not only breaks up the material into smaller particles but alters the nature of the original parent rock itself. The main processes responsible are hydration, oxidation, and carbonation. New compounds are formed due to chemical alterations.
Rainwater that comes in contact with the rock surface reacts to form hydrated oxides, carbonates and sulfates. If there is a volume increase, the disintegration continues. Due to leaching, water-soluble materials are washed away and rocks lose their cementing properties.
Chemical weathering occurs in wet and warm conditions and consists of degradation by decomposition and/or alteration. The results of chemical weathering are generally fine soils with altered mineral grains.
The effects of weathering and transportation mainly determine the basic nature of the soil (size, shape, composition, and distribution of the particles).
The environment into which deposition takes place, and the subsequent geological events that take place there, determine the state of the soil (density, moisture content) and the structure or fabric of the soil (bedding, stratification, occurrence of joints or fissures)
Transportation agencies can be combinations of gravity, flowing water or air, and moving ice. In water or air, the grains become sub-rounded or rounded, and the grain sizes get sorted so as to form poorly-graded deposits. In moving ice, grinding and crushing occur, size distribution becomes wider forming well-graded deposits.
In running water, soil can be transported in the form of suspended particles, or by rolling and sliding along the bottom. Coarser particles settle when a decrease in velocity occurs, whereas finer particles are deposited further downstream. In still water, horizontal layers of successive sediments are formed, which may change with time, even seasonally or daily.
Wind can erode, transport and deposit fine-grained soils. Wind-blown soil is generally uniformly graded.
A glacier moves slowly but scours the bedrock surface over which it passes.
Gravity transports materials along slopes without causing many alterations.







No comments:
Post a Comment
If you are getting more information from civilengineerfriend page please give your comments. Share the page information in your whatsapp group. Subscribe our page to get more information.