Moulding:
The clay which is prepared as above is then sent for the
text operation of moulding.Following are two types of moulding:
i. Hand Moulding
ii. Machine Moulding
Hand moulding:
In hand moulding , the bricks are moulded by hand i.e.; manually. It is adopted where
manpower is cheap and is readily available for the manufacturing process of
bricks ona small scale.The moulds are rectangular boxes which are open at top
and bottom.They may be of wood or steel.It should be beprepared from
well-seasonedwood. The longer sides are kept slightly projecting to serve as
handles. The strips of brass or steel are sometimes fixed on the edges of
wooden moulds to make them more durable.It is prepared from the combination of
steel plate and channel. It may even be prepared from steel angles and plates.
Thethickness of steel mould is 6mm.They is used for manufacturing bricks on
alarge scale. The steel moulds are more durable than wooden one and turn out
bricks of uniform size.The bricks shrink during drying and burning .Hence the
mouldsare therefore made larger than burnt bricks (812%).
The bricks prepared by hand moulding are of two types:
Ground mouldedand Tablemoulded
1.It indicates the trade name of the manufacturer
2.In brick work, the bricks are laid with frog uppermost.
It thus affords a key for mortar when the next brick is placed over it.
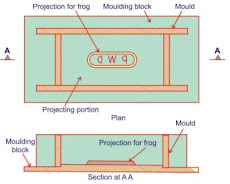
The ground moulded bricks of better quality and with frogs
on their surface are made by using a pair of pallet boards and a wooden block.
A pallet is a piece of thin wood.The block is bigger than the mould and it has
projection of about 6mm height on its surface.The dimensions of projection
correspond to internal dimensions of mould.The design of impression or frog is
made on this block.The wooden block is also known as the moulding block or
stock board.
The mould is placed to fit in the projection of wooden
block and clay is then dashed inside the mould.A pallet is placed on the top
and the whole thing is then turn upside down.The mould is taken out and placed
over the raw brick and it is conveyed to the drying sheds.The bricks are placed to stand on their longer
sides in drying sheds and pallet boards are brought back for using them again.As the bricks are laid on edge,
they occupyless space and they dry
quicker and better.
Table Moulded Bricks:
i) The
process of moulding of bricks is just similar as above.But in this case, the
mould stands near a table size 2m x 1m. The bricks are moulded on the table and
send for further process of drying.
ii) However the efficiency of the moulder gradually decreases because of standing at some place for a longer duration.The cost of brick is also increases when table moulding is adopted.
Machine Moulding:
This type of moulding is carried out by two processes:
i) Plastic clay machine
ii) Dry clay machine
Plastic Clay Moulding
i)
Such machine consists of a rectangular opening
having length and width is equal to an ordinary bricks. The pugged clay is
placed in the machine and it comes out through the rectangular opening.
ii)
These are cut into strips by the wire fixed at the
frame. The arrangement is made in such a way that the strips thickness is equal
to that of the bricks are obtained. So it is also called as
WIRE CUT BRICKS.
Dry Clay Machinemoulding:
In these machines, the strong clay is finally converted in
to powered form.A small quantity of water is then added to form a stiff plastic
paste.
ii) Such paste is placed in mould and pressed by machine to
form dry and well-shaped bricks. They do not require the process of drying.
Drying
The damp bricks, if brunt,are likely to be cracked and
distorted.Hence the moulded bricks are dried before they are taken for the next
operation of burning. For the drying the bricks are laid longitudinally in the
stacks of width equal to two bricks,A stack consists of ten or eight tiers.The
bricks are laid along and across the stock in alternate layers. All the bricks
are placed on edges. The bricks are allowed to dry until the bricks are become
leather hard of moisture content about 2%.
Burning
Bricks
are burned at high temperature to gain the strength, durability, density and
red color appearance.All the water is removed at the temperature of 650 degrees
but they are burnt at an temperature of about 1100 degrees because the fusing
of sand and lime takes place at this temperature and chemical bonding takes
between these materials after the temperature is cooled down resulting in the
hard and dense mass.
Bricks
are not burnt above this temperature because it will result in the melting of
the bricks and will result in a distorted shape and a very hard mass when
cooled which will not be workable while brickwork. Bricks can be burnt using
the following methods:
(a)
Clamp Burning
(b) Kiln Burning
Clamp
Burning:
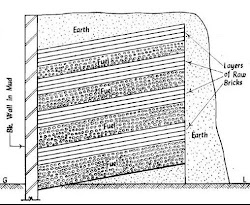
Clamp is a temporary structure generally constructed over the ground with a height of about 4 to 6 m. It is employed when the demand of the bricks is lower scale and when it is not a monsoon season. This is generally trapezoidal in plan whose shorter edge among the parallel sides is below the ground and then the surface raising constantly at about 15 degrees to reach the other parallel edge over the ground.A vertical brick and mud wall is constructed at the lower edge to support the stack of the brick. First layer of fuel is laid as the bottom most layer with the coal, wood and other locally available material like cow dung and husk.Another layer of about 4 to 5 rows of bricks is laid and then again a fuel layer is laid over it. The thickness of the fuel layer goes on with the height of the clamp.
After
these alternate layers of the bricks and fuel the top surface is covered with
the mud so as to preserve the heat.Fire is ignited at the bottom, once fire is
started it is kept under fire by itself for one or two months and same time
period is needed for the cooling of the bricks.
Disadvantages
of Clamp burning:
1.
Bricks at the bottom
are over-burnt while at the top are under-burnt.
2.
Bricks loose their
shape, and reason may be their descending downward once the fuel layer is
burnt.
3.
This method cannotemploy
for the manufacturing of large number of bricks and it is costly in terms of
fuel because large amount of heat is wasted.
4.
It cannot be
employed in monsoon season.
Kiln
Burning:
Kiln
is a large oven used for the burning of bricks. Generally coal and other
locally available materials like wood, cow dung etc can be used as fuel. They
are of two types:
• Intermittent
Kilns.
• Continuous Kilns.
Intermittent Kilns: these are also the periodic kind of kilns, because in
such kilns only one process can take place at one time. Various major processes
which takes place in the kilns are:Loading,
unloading, Cooling, and Burning of bricks.
There
are two kind of intermittent kilns:
(i)
Up-draught
Intermittent Kilns
(ii)
Down draught
Intermittent Kilns
Down draught kilns are more efficient because the heat is utilized more by moving the hot gases in the larger area of the kiln. In up draught kilns the hot gases are released after they rise up to chimney entrance.
Continuous
Kilns:
These
kilns are called continuous because all the processes of loading, unloading,
cooling, heating, pre-heating take place simultaneously. They are used when the
bricks are demanded in larger scale and in short time. Bricks burning are
completed in one day, so it is a fast method of burning.There are two
well-known continuous kilns:
Bull's
Trench Kiln:Bull's trench kiln
consists of a rectangular, circular or oval plan shape. They are constructed
below the ground level by excavating a trench of the required width for the
given capacity of brick manufacturing.This Trench is divided generally in 12
chambers so that 2 numbers of cycles of brick burning can take place at the
same time for the larger production of the bricks. Or it may happen that one
cycle is carried out at one time in all the 12 chambers by using a single
process in the 2-3 chambers at the same time.The structure is under-ground so
the heat is conserved to a large extent so it is more efficient. Once fire is started it constantly travels
from one chamber to the other chamber, while other operations like loading,
unloading, cooling, burning and preheating taking place simultaneously.
Such
kilns are generally constructed to have a manufacturing capacity of about
20,000 bricks per day. The drawback of this kiln is that there is not a
permanent roof, so it is not easy to manufacture the bricks in the monsoon
seasons.
Hoffman's
Kiln:The main difference between the
Bull's trench kiln and the Hoffman kilns are:
1.
Hoffman's kiln is an over the ground structure while Bull's Trench Kiln is an
underground structure.
2.Hoffman's
kiln have a permanent roof while Bull's trench Kiln do not have so it former
can be used in 12 months a year to manufacture bricks but later is stopped in
the monsoon season.
Hoffman's
kiln is generally circular in plan, and is constructed over the ground. The
whole structure is divided into the 12 chambers and the entire processes takes
place simultaneously like in Bull's trench Kiln.










No comments:
Post a Comment
If you are getting more information from civilengineerfriend page please give your comments. Share the page information in your whatsapp group. Subscribe our page to get more information.