DMC piling method procedure
Direct Mud Circulation method of pile foundation installation is used for bored cast in-situ piles. Direct Mud Circulation method is best suited when working-space is a huge constraint. In Industries and power plants where there is a labyrinth of pipelines snaking all around, DMC comes to the rescue.The whole project report is subdivided in the following
sections:
1. Introduction
2. Objectives and classification of piles and piling
methods
3. Principle of DMC piling
4. Apparatus used
5. Field procedure DMC piling
6. Conclusion
1. INTRODUCTION
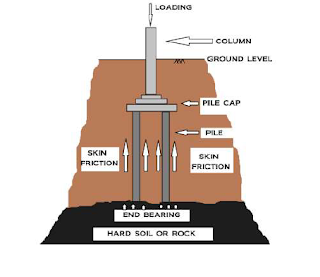
Piles are the columnar structure, the most common type of
deep foundation, that safely transfer loads from the super
structure to more competent subsurface strata by means of
friction, end bearing or a combination of both. Piles can be
broadly classified based on the following parameters.
1. Method of installation of piles – Driven (displacement) piles
or bored (replacement) piles.
2. Type of material used for piling – Concrete, steel, timber
piles etc.
Among these, concrete piles can be classified further as precast
and cast in situ concrete piles. Though there are a variety
of piling options, the most common type of piles used for
majority of construction works in India are bored cast in situ
concrete piles.
2. Objectives and classification of piles and piling methods Functions of piles:
The major uses of piles are:
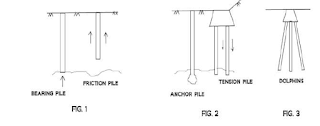
1. To carry vertical compression load, eg. bearing piles,
friction pile. (FIG. 1)
2. To resist uplift pressure, eg. tension piles or uplift piles or
anchor piles. (FIG. 2)
3. To resist horizontal or inclined loads, eg. Batter piles.
(FIG. 3)
Setting up piles
Depending up on the setting up principle, piles can be of two types, eg. Displacement type and Replacement type, each has its own advantages and disadvantages. For displacement piling
method, piles are driven into the ground pushing the soil out of its way. Displacement piling is good for contaminated sites where it costs a lot to move the soil out.
Using the replacement piling method, muck is dug out and replaced with the pile. Much bigger piles can be casted by replacement method.
Direct Mud Circulation (DMC) piling method or simply DMC Piling method is an example of replacement piling method. This method is the principle subject of interest in this report.
The advantages of displacement piling are:-
Self testing as driven to refusal or "set"
No pile arising to dispose of
Little disturbance
Limited access
High production
The disadvantages of displacement piling are:-
Cannot penetrate obstructions
Cannot always penetrate desiccated clay
Vibration and noise may be an issue
The advantages of replacement piling are:-
Effectively vibration free
Installed into non cohesive and water bearing soils
High production
Restricted access
The main disadvantage of replacement piling is that:-
it produces excavated material which requires removal off site
3. Principle of DMC piling
DMC piling is a typical wash bored piling method, ie. the piles are of REPLACEMENT type. For this type of piling method, the sub soil must be of cohesive nature. The basic principle of DMC piling
lies in the fact that the soil layers becomes harder to penetrate with depth, so to soften the hard soil layers deep below the ground level,water jet streams are used and then a typical chisel cuts the
relatively softer soil. Bore holes of several depths (for example 10m,15m, 20m, 25m, 30m, etc.) and diameter (for example 500mm 750mm, 1000mm etc.) are dug as per design requirements. It can be
understood quite clearly that the nearby soil can collapse. To prevent the collapse some special safety measures are considered during the operation which will be discussed in later sections. After the bore hole is dug and the collapse of subsoil around the hole is safely prohibited, a reinforcement cage is entered into the borehole and concrete is filled from the bottom of the hole with the help of pipes, typically designed for this operation, called the Tremie pipes. Usually concrete is left 28 days to harden and gain full strength, but sometimes using admixtures they are prepared within 21 days.
4. Apparatus used
I. DMC rig
THE TRIPOD SYSTEM
Main shear leg: it is the longer leg than the other two that carries the load.
The length is 7.5m. The length can be adjusted. With the help of 20mm dia pins
The side shear legs: there are two side shear legs, 6.3m long
and they mainly support the tripod system.
The side legs must be placed at least 1.5m away from the centre
of the piles.
BASE CHANNEL
These are standard I section, 2cm thick and there are grooving in it that holds the shear legs onto the ground with the help of base cannel pin.
•
SLIP OVER WHEEL
Diameter
|
450mm
|
Thickness
|
50mm
|
Operation
|
The rope slips over this
wheel or Pulley
|
 | ||||||
• S.O. WHEEL
PIN
SLIP OVER WHEEL • SLIP OVER WEEL HOLDER
Diameter = 500 • PLUNGE
Inside Diameter = 50mm
• SUSPENSION
PLATE – this is called into action if somehow the chisel is stuck in the
borehole. Pulleys are attached here and the chisel is pulled out.
|
Suspension Plate
• MAIN SHEAR
LEG PIN – 20mm dia.
II. Winch
Capacity
|
3 Ton (Other
capacities can be of
1 Ton 2.5
Ton 5 Ton 7.5 Ton etc.)
|
Driven wheel diameter
|
900mm
|
II. Diesel engine • USED IN
WINCH (RUSTON MAKE)
Number of cylinder
|
4
|
3
|
Diesel consumption
|
2.1 lit/hr
|
1.75 lit/hr
|
Mobil
consumption (fresh engine)
|
0.5 lit per 7 days
|
0.5 lit per
7 days
|
Mobil
consumption (older engine)
|
0.5 lit per 12 hours
|
0.5 lit per
12 hours
|
• USED IN
PUMP (KILOSKER MAKE)
Number of cylinder
|
2
|
Diesel consumption
|
1.25 lit/hr
|
Mobil consumption
|
250ml per 12
hours
|
IV. Bailer or Slush Pump
Length
2700mm
|
Inside
Diameter
450mm
|
Weight
0.5 Ton
|
V. Guide casing
Length
2750mm
|
Inside
Diameter
550mm
|
Thickness of
casing
30mm
|
Thickness of
collar
20mm
|
Thickness of
sheet
80mm
|
Inside
Diameter
400mm
|
Length
2500mm
|
Number of
nozzle
4
|
7. DMC rod
Length (m)
|
2.7 3 3.25
|
Diameter (mm)
|
95 75 65
|
Thread length (mm)
|
120
|
Thread type
|
Tapered
|
ID of tapered king end
(mm)
|
80
|
ID of queen end (mm)
|
120
|
Tapered thread
end of DMC rods
7.
Rope
Diameter – 20mm
8.
Tremie pipe
ID
|
5 inch
|
OD
|
6 inch
|
Thickness of sheet
|
12mm
|
9.
Vertical
pump
Power source
|
Electrically
operated
|
Power
|
10 Hp
|
10.
Bentonite
tank and Bentonite slurry
The Bentonite tank stores the Bentonite water which is
of avg. Density of 1.04gm/cc. The minimum density is 1.03gm/cc and maximum
density is 1.05gm/cc
Vertical Pump in Bentonite tank
7.
Wash vat
This is where the muck mix with water gets stored, the
muck gets precipitated and the water becomes reusable.
8.
Tremie fork
Used
to insert the tremie pipes and taking out DMC rods.
5.
Field
procedure DMC piling
• For
executing DMC piling method which is approved as per IS 2911 under
specifications of bored cast in situ piles. The positioning of points where the
piles are proposed to set up, are checked by the surveyor.
Ø DMC piling Rig set-up and initiation of boring
using the Bailer
• After
the point for boring operation is set out by the surveyor the tripod is paced
such that each side legs are at least 1.5m away from the point, keeping the
centre of borehole exactly in the centre.
• The
bailer is then attached with the rope and the boring operation is initiated.
• After
bailer reaches its full length into the soil, the guide casing is inserted into
the hole for farther operations.
Insertion of the guide casing
To
prevent the side collapse and caving in, a guide casing of 550mm dia and of
2750mm length is placed on the top of the bore hole and hammered by the bailer
to insert it into the soil. This will be withdrawn after concreting is over.
Ø Boring with Chisel
• Once
the guide casing is placed, the boring is started with chisel.
• The
chisel has 4 nozzles from where water jet is forced on the hard soil layer as
the boring progresses.
Ø
Progression of boring and addition of DMC rods
• DMC
rods are added one after another as the depth increases.
• The
DMC head are attached on top of the DMC rods which has the plunge which
receives the water from delivery hose.
• The
whole system is pulled up by the rope and the D-Shackle with the help of the
winch system and then left to fall free, so that the chisel at the bottom cuts
the soil and the boring progresses.
• The
loose soil produced by boring, mixes with water and comes up and is stored in
the wash vat, where the soil gets precipitated and the water is again
usable.
Ø
Taking out of the DMC rods and Chisel and Insertion of the reinforcement
cage
• After
the boring is complete up to the desired depth, the DMC rods are removed one by
one using the DMC fork and the chisel is also removed.
• Then
the steel reinforcement cage is inserted and welded where ever there are
joints.
Ø
Concreting
and finalization of the process
• The tremie
pipes are inserted one by one using the Tremie fork and then the bore hole is
washed with the Bentonite water and the Muck is completely removed and the hole
is filled with bentonite slurry.
• The Transit
mixer arrives and the Hopper is attached on top of the tremie pipe.
• The TM puts
concrete mix into the hopper and the valve opens. The bore hole is gradually
filled with concrete which is
compacted by gradual vibration of tremie pipes. This
filling of concrete from the bottom is done to avoid segregation of the
concrete mix.
• As the
concrete fills the hole from bottom, Bentonite slurry escapes the hole. The
tremie pipes are detached one by one and thus the hole gets filled completely.
• After the
hole is fully filled, the concrete is left 28 days to gain full strength. After
28 days the guide casing is removed and the pile is ready.
6. Conclusion
DMC
piling is the most common piling methods used in India. For moderate sized
piles, that is 450mm to 1000mm diameter and 25m to 30m depth piles; it is also
most convenient and economic way of piling. Larger piles that are of diameter
up to 1500mm can also be founded by this method, but those are not that convenient.
Other process like Reduced Mud Circulation (RMC) is also in use.













No comments:
Post a Comment
If you are getting more information from civilengineerfriend page please give your comments. Share the page information in your whatsapp group. Subscribe our page to get more information.